Timothy Wilken
The following article was forwarded by SynEARTH reader Dexter Graphic. I was first put off by the title, but when I took the time to read it more carefully, I found it very interesting.
The author is an Italian economist who makes the point that humans make four types of decisions. They can chose an intelligent action where they win and others win. They can chose a helpless action where they lose and others win. They can choose a bandit action where they win and others lose. Or, they can choose a stupid action where they lose and others lose.
He further implies that humans are their choices, and so identifies them as intelligent, helpless, bandit, or stupid.
As a human intelligence scientist, I would argue with the value of this identification, I think all humans make all of these choices sometimes in their lives. Sometimes I act intelligently, sometimes helplessly, sometimes banditly, and sometimes stupidly. The author acknowledges this inconsistency of action below in the section titled Frequency Distribution, but his language still implies the identification. While many humans are caught in a rut, and habitually make the same type of choices over and over again. We should still avoid the error of identification. Humans are not their behavior, and remain capable of making better choices in the future. This is the only basis for viewing the future with some optimism.
This 1987 article is reposted from Gandalf.
Carlo M. Cipolla
The First Basic Law
The first basic law of human stupidity asserts without ambiguity that:
Always and inevitably everyone underestimates the number of stupid individuals in circulation.
At first, the statement sounds trivial, vague and horribly ungenerous. Closer scrutiny will however reveal its realistic veracity. No matter how high are one’s estimates of human stupidity, one is repeatedly and recurrently startled by the fact that:
a) people whom one had once judged rational and intelligent turn out to be unashamedly stupid.
b) day after day, with unceasing monotony, one is harassed in one’s activities by stupid individuals who appear suddenly and unexpectedly in the most inconvenient places and at the most improbable moments.
The First Basic Law prevents me from attributing a specific numerical value to the fraction of stupid people within the total population: any numerical estimate would turn out to be an underestimate. Thus in the following pages I will denote the fraction of stupid people within a population by the symbol sigma.
The Second Basic Law
Cultural trends now fashionable in the West favour an egalitarian approach to life. People like to think of human beings as the output of a perfectly engineered mass production machine. Geneticists and sociologists especially go out of their way to prove, with an impressive apparatus of scientific data and formulations that all men are naturally equal and if some are more equal than others, this is attributable to nurture and not to nature. I take an exception to this general view. It is my firm conviction, supported by years of observation and experimentation, that men are not equal, that some are stupid and others are not, and that the difference is determined by nature and not by cultural forces or factors. One is stupid in the same way one is red-haired; one belongs to the stupid set as one belongs to a blood group. A stupid man is born a stupid man by an act of Providence. Although convinced that fraction of human beings are stupid and that they are so because of genetic traits, I am not a reactionary trying to reintroduce surreptitiously class or race discrimination. I firmly believe that stupidity is an indiscriminate privilege of all human groups and is uniformly distributed according to a constant proportion. This fact is scientifically expressed by the Second Basic Law which states that
The probability that a certain person be stupid is independent of any other characteristic of that person.
In this regard, Nature seems indeed to have outdone herself. It is well known that Nature manages, rather mysteriously, to keep constant the relative frequency of certain natural phenomena. For instance, whether men proliferate at the Northern Pole or at the Equator, whether the matching couples are developed or underdeveloped, whether they are black, red, white or yellow the female to male ratio among the newly born is a constant, with a very slight prevalence of males. We do not know how Nature achieves this remarkable result but we know that in order to achieve it Nature must operate with large numbers. The most remarkable fact about the frequency of stupidity is that Nature succeeds in making this frequency equal to the probability quite independently from the size of the group.
Thus one finds the same percentage of stupid people whether one is considering very large groups or one is dealing with very small ones. No other set of observable phenomena offers such striking proof of the powers of Nature.
The evidence that education has nothing to do with the probability was provided by experiments carried on in a large number of universities all over the world. One may distinguish the composite population which constitutes a university in five major groups, namely the blue-collar workers, the white-collar employees, the students, the administrators and the professors.
Whenever I analyzed the blue-collar workers I found that the fraction sigma of them were stupid. As sigma’s value was higher than I expected (First Law), paying my tribute to fashion I thought at first that segregation, poverty, lack of education were to be blamed. But moving up the social ladder I found that the same ratio was prevalent among the white-collar employees and among the students. More impressive still were the results among the professors. Whether I considered a large university or a small college, a famous institution or an obscure one, I found that the same fraction sigma of the professors are stupid. So bewildered was I by the results, that I made a special point to extend my research to a specially selected group, to a real elite, the Nobel laureates. The result confirmed Nature’s supreme powers: sigma fraction of the Nobel laureates are stupid.
This idea was hard to accept and digest but too many experimental results proved its fundamental veracity. The Second Basic Law is an iron law, and it does not admit exceptions. The Women’s Liberation Movement will support the Second Basic Law as it shows that stupid individuals are proportionately as numerous among men as among women. The underdeveloped of the Third World will probably take solace at the Second Basic Law as they can find in it the proof that after the developed are not so developed. Whether the Second Basic Law is liked or not, however, its implications are frightening: the Law implies that whether you move in distinguished circles or you take refuge among the head-hunters of Polynesia, whether you lock yourself into a monastery or decide to spend the rest of your life in the company of beautiful and lascivious women, you always have to face the same percentage of stupid people—which percentage (in accordance with the First Law) will always surpass your expectations.
The Third (and Golden) Basic Law
The Third Basic Law assumes, although it does not state it explicitly, that human beings fall into four basic categories: the helpless, the intelligent, the bandit and the stupid. It will be easily recognized by the perspicacious reader that these four categories correspond to the four areas I, H, S, B, of the basic graph (see below).
Figure 1
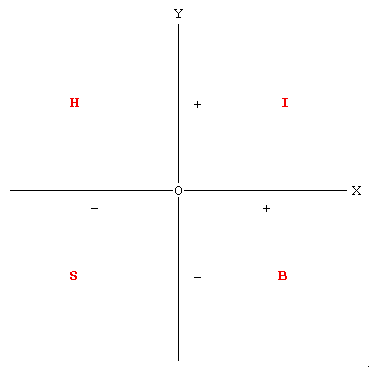
If Tom takes an action and suffers a loss while producing a gain to Dick, Tom’s mark will fall in field H: Tom acted helplessly. If Tom takes an action by which he makes a gain while yielding a gain also to Dick, Tom’s mark will fall in area I: Tom acted intelligently. If Tom takes an action by which he makes a gain causing Dick a loss, Tom’s mark will fall in area B: Tom acted as a bandit. Stupidity is related to area S and to all positions on axis Y below point 0. As the Third Basic Law explicitly clarifies:
A stupid person is a person who causes losses to another person or to a group of persons while himself deriving no gain and even possibly incurring losses.
When confronted for the first time with the Third Basic Law, rational people instinctively react with feelings of skepticism and incredulity. The fact is that reasonable people have difficulty in conceiving and understanding unreasonable behaviour. But let us abandon the lofty plane of theory and let us look pragmatically at our daily life. We all recollect occasions in which a fellow took an action which resulted in his gain and our loss: we had to deal with a bandit. We also recollect cases in which a fellow took an action which resulted in his loss and our gain: we had to deal with a helpless person. We can recollect cases in which a fellow took an action by which both parties gained: he was intelligent. Such cases do indeed occur. But upon thoughtful reflection you must admit that these are not the events which punctuate most frequently our daily life. Our daily life is mostly, made of cases in which we lose money and/or time and/or energy and/or appetite, cheerfulness and good health because of the improbable action of some preposterous creature who has nothing to gain and indeed gains nothing from causing us embarrassment, difficulties or harm. Nobody knows, understands or can possibly explain why that preposterous creature does what he does. In fact there is no explanation—or better there is only one explanation: the person in question is stupid.
Frequency Distribution
Most people do not act consistently. Under certain circumstances a given person acts intelligently and under different circumstances the same person will act helplessly. The only important exception to the rule is represented by the stupid people who normally show a strong proclivity toward perfect consistency in all fields of human endeavours.
From all that proceeds, it does not follow, that we can chart on the basic graph only stupid individuals. We can calculate for each person his weighted average position in the plane of figure 1 quite independently from his degree of inconsistency. A helpless person may occasionally behave intelligently and on occasion he may perform a bandit’s action. But since the person in question is fundamentally helpless most of his action will have the characteristics of helplessness. Thus the overall weighted average position of all the actions of such a person will place him in the H quadrant of the basic graph.
The fact that it is possible to place on the graph individuals instead of their actions allows some digression about the frequency of the bandit and stupid types.
The perfect bandit is one who, with his actions, causes to other individuals losses equal to his gains. The crudest type of banditry is theft. A person who robs you of 100 pounds without causing you an extra loss or harm is a perfect bandit: you lose 100 pounds, he gains 100 pounds. In the basic graph the perfect bandits would appear on a 45-degree diagonal line that divides the area B into two perfectly symmetrical sub-areas (line 0-M).
Figure 2
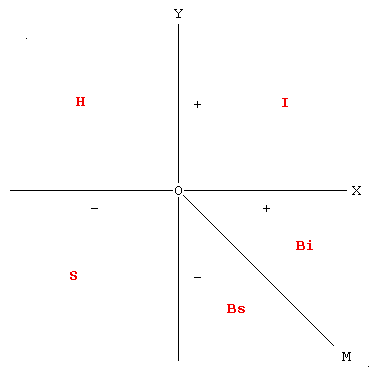
However the “perfect” bandits are relatively few. The line 0-M divides the area B into two sub-areas, B1, and B2, and by far the largest majority of the bandits falls somewhere in one of these two sub-areas.
The bandits who fall in area B1 are those individuals whose actions yield to them profits which are larger than the losses they cause to other people. All bandits who are entitled to a position in area B1 are bandits with overtones of intelligence and as they get closer to the right side of the X axis they share more and more the characteristics of the intelligent person.
Unfortunately the individuals entitled to a position in the B1 area are not very numerous. Most bandits actually fall in area B2. The individuals who fall in this area are those whose actions yield to them gains inferior to the losses inflicted to other people. If someone kills you in order to rob you of fifty pounds or if he murders you in order to spend a weekend with your wife at Monte Carlo, we can be sure that he is not a perfect bandit. Even by using his values to measure his gains (but still using your values to measure your losses) he falls in the B2 area very close to the border of sheer stupidity. Generals who cause vast destruction and innumerable casualties in return for a promotion or a medal fall in the same area.
The frequency distribution of the stupid people is totally different from that of the bandit. While bandits are mostly scattered over an area stupid people are heavily concentrated along one line, specifically on the Y axis below point O. The reason for this is that by far the majority of stupid people are basically and unwaveringly stupid—in other words they perseveringly insist in causing harm and losses to other people without deriving any gain, whether positive or negative.
There are however people who by their improbable actions not only cause damages to other people but in addition hurt themselves. They are a sort of super-stupid who, in our system of accounting, will appear somewhere in the area S to the left of the Y axis.
The Power of Stupidity
It is not difficult to understand how social, political and institutional power enhances the damaging potential of a stupid person. But one still has to explain and understand what essentially it is that makes a stupid person dangerous to other people—in other words what constitutes the power of stupidity.
Essentially stupid people are dangerous and damaging because reasonable people find it difficult to imagine and understand unreasonable behaviour. An intelligent person may understand the logic of a bandit. The bandit’s actions follow a pattern of rationality: nasty rationality, if you like, but still rationality. The bandit wants a plus on his account. Since he is not intelligent enough to devise ways of obtaining the plus as well as providing you with a plus, he will produce his plus by causing a minus to appear on your account. All this is bad, but it is rational and if you are rational you can predict it. You can foresee a bandit’s actions, his nasty manoeuvres and ugly aspirations and often can build up your defenses.
With a stupid person all this is absolutely impossible as explained by the Third Basic Law. A stupid creature will harass you for no reason, for no advantage, without any plan or scheme and at the most improbable times and places. You have no rational way of telling if and when and how and why the stupid creature attacks. When confronted with a stupid individual you are completely at his mercy. Because the stupid person’s actions do not conform to the rules of rationality, it follows that:
a) one is generally caught by surprise by the attack; b) even when one becomes aware of the attack, one cannot organize a rational defense, because the attack itself lacks any rational structure.
The fact that the activity and movements of a stupid creature are absolutely erratic and irrational not only makes defense problematic but it also makes any counter-attack extremely difficult—like trying to shoot at an object which is capable of the most improbable and unimaginable movements. This is what both Dickens and Schiller had in mind when the former stated that “with stupidity and sound digestion man may front much” and the latter wrote that “against stupidity the very Gods fight in vain.”
The Fourth Basic Law
That helpless people, namely those who in our accounting system fall into the H area, do not normally recognize how dangerous stupid people are, is not at all surprising. Their failure is just another expression of their helplessness. The truly amazing fact, however, is that also intelligent people and bandits often fail to recognize the power to damage inherent in stupidity. It is extremely difficult to explain why this should happen and one can only remark that when confronted with stupid individuals often intelligent men as well as bandits make the mistake of indulging in feelings of self-complacency and contemptuousness instead of immediately secreting adequate quantities of adrenaline and building up defenses.
One is tempted to believe that a stupid man will only do harm to himself but this is confusing stupidity with helplessness. On occasion one is tempted to associate oneself with a stupid individual in order to use him for one’s own schemes. Such a manoeuvre cannot but have disastrous effects because a) it is based on a complete misunderstanding of the essential nature of stupidity and b) it gives the stupid person added scope for the exercise of his gifts. One may hope to outmanoeuvre the stupid and, up to a point, one may actually do so. But because of the erratic behaviour of the stupid, one cannot foresee all the stupid’s actions and reactions and before long one will be pulverized by the unpredictable moves of the stupid partner.
This is clearly summarized in the Fourth Basic Law which states that:
Non-stupid people always underestimate the damaging power of stupid individuals. In particular non-stupid people constantly forget that at all times and places and under any circumstances to deal and/or associate with stupid people always turns out to be a costly mistake.
Through centuries and millennia, in public as in private life, countless individuals have failed to take account of the Fourth Basic Law and the failure has caused mankind incalculable losses.
The Fifth Basic Law
Instead of considering the welfare of the individual let us consider the welfare of the society, regarded in this context as the algebraic sum of the individual conditions. A full understanding of the Fifth Basic Law is essential to the analysis. It may be parenthetically added here that of the Five Basic Laws, the Fifth is certainly the best known and its corollary is quoted very frequently. The Fifth Basic Law states that:
A stupid person is the most dangerous type of person.
The corollary of the Law is that:
A stupid person is more dangerous than a bandit.
The result of the action of a perfect bandit (the person who falls on line OM of figure 2) is purely and simply a transfer of wealth and/or welfare. After the action of a perfect bandit, the bandit has a plus on his account which plus is exactly equivalent to the minus he has caused to another person. The society as a whole is neither better nor worse off. If all members of a society were perfect bandits the society would remain stagnant but there would be no major disaster. The whole business would amount to massive transfers of wealth and welfare in favour of those who would take action. If all members of the society would take action in regular turns, not only the society as a whole but also individuals would find themselves in a perfectly steady state of no change.
When stupid people are at work, the story is totally different. Stupid people cause losses to other people with no counterpart of gains on their own account. Thus the society as a whole is impoverished. The system of accounting which finds expression in the basic graphs shows that while all actions of individuals falling to the right of the line P-0-M (see fig. 3) add to the welfare of a society; although in different degrees, the actions of all individuals falling to the left of the same line P-0-M cause a deterioration.
Figure 3
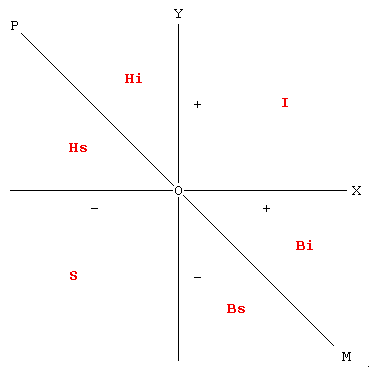
In other words the helpless with overtones of intelligence (area H1), the bandits with overtones of intelligence (area B1) and above all the intelligent (area I) all contribute, though in different degrees, to accrue to the welfare of a society. On the other hand the bandits with overtones of stupidity (area B2) and the helpless with overtones of stupidity (area H1) manage to add losses to those caused by stupid people thus enhancing the nefarious destructive power of the latter group.
All this suggests some reflection on the performance of societies. According to the Second Basic Law, the fraction of stupid people is a constant sigma which is not affected by time, space, race, class or any other socio-cultural or historical variable. It would be a profound mistake to believe the number of stupid people in a declining society is greater than in a developing society. Both such societies are plagued by the same percentage of stupid people. The difference between the two societies is that in the society which performs poorly:
a) the stupid members of the society are allowed by the other members to become more active and take more actions; b) there is a change in the composition of the non-stupid section with a relative decline of populations of areas I, H1 and B1 and a proportionate increase of populations H2 and B2.
This theoretical presumption is abundantly confirmed by an exhaustive analysis of historical cases. In fact the historical analysis allows us to reformulate the theoretical conclusions in a more factual way and with more realistic detail.
Whether one considers classical, or medieval, or modern or contemporary times one is impressed by the fact that any country moving uphill has its unavoidable sigma fraction of stupid people. However the country moving uphill also has an unusually high fraction of intelligent people who manage to keep the sigma fraction at bay and at the same time produce enough gains for themselves and the other members of the community to make progress a certainty.
In a country which is moving downhill, the fraction of stupid people is still equal to sigma; however in the remaining population one notices among those in power an alarming proliferation of the bandits with overtones of stupidity (sub-area B1 of quadrant B in figure 3) and among those not in power an equally alarming growth in the number of helpless individuals (area H in basic graph, fig.1). Such change in the composition of the non-stupid population inevitably strengthens the destructive power of the sigma fraction and makes decline a certainty. And the country goes to Hell.
For fifteen years it was very difficult to find the original English text of Carlo Cipolla’s Laws of Human Stupidity. But now it’s available online in a few places, such as Mentalsoup and Ecotopia. Those online texts include some “funny” drawings by James Donnelly, replaced here by the straightforward graphs that were included in the Italian edition published by Il Mulino in 1988. (May 2002)
See also The Power of Stupidity